Model Software
QMRAcatch
Simulating concentrations of health-related microbes/viruses in rivers and river/floodplain systems: integrating faecal indicator, MST-marker, and pathogen data to elucidate optimal catchment protection and treatment requirements (log-reductions) for health-related water safety management
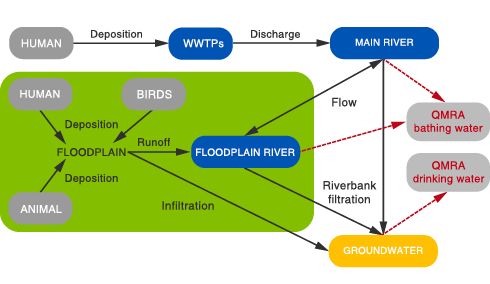
The Interuniversity Cooperation Centre for Water and Health (ICC Water & Health) and the Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) jointly developed an interactive user-friendly computational tool, QMRAcatch, for simulating microbial concentrations in a river and a river/floodplain including quantitative microbial risk assessment (QMRA).
The model domain encompasses various human/animal contamination sources (domestic wastewater, faecal pollution from animals, birds and humans). Best available data on faecal indicator bacteria (FIB), genetic microbial source tracking (MST) marker, and reference pathogens can be combined to support source-targeted calibration and verification of the model.
Additional reference pathogens can be selected (based on assumed source concentrations from literature) to support cross-comparison of pathogen risks. The importance of critical factors and/or future changes (e.g. hydrological/climatic situation, animal/human pollution sources, epidemiology) can be considered by scenario analysis.
Results inform about sustainable catchment protection measures and required pathogen reduction targets (log-reductions of pathogens during treatment/disinfection) to meet defined health-based targets (based on a maximum tolerable infection risk). In addition to drinking water safety management, infection risks associated during recreation/bathing activities can also be considered by the software tool for the investigated environment.
Although developed for Austria, QMRAcatch can be applied by drinking water companies, researchers, and policy makers worldwide to support pro-active water safety management.
Downloads
In the download section you will find the original Mathematica version of QMRAcatch, Free CDF Player, Spreadsheet with microbial data (Example), QMRAcatch Quick User Guide, Spreadsheet with settings and simulations (Example), Spreadsheet with hydrologic data (Example). The source code for QMRAcatch v 1.0 python (Demeter et al. 2021) and QMRAcatch v 1.1 python backwater (Derx et al. 2021) is available upon request (derx@hydro.tuwien.ac.at).
Publikationen
Schijven, J. F., J. Derx, A. M. de Roda Husman, A. P. Blaschke, and A. H. Farnleitner, 2015. QMRAcatch: Microbial quality simulation of water resources including infection risk assessment. J. Env. Qual. 44(5), pp. 1491-1502, doi: 10.2134/jeq2015.01.0048
Derx, J., J. Schijven, R. Sommer, C.M. Zoufal-Hruza, I.H. van Driezum, G. Reischer, S. Ixenmaier, A.K.T. Kirschner, C. Frick, A.M. de Roda Husman, A.H. Farnleitner, and A.P. Blaschke, 2016. QMRAcatch: Human-associated faecal pollution and infection risk modelling for a river/floodplain environment. Journal of Environmental Quality 45(4), pp. 1205-1214, doi:10.2134/jeq2015.11.0560
Demeter*, K., Derx*, J., Komma, J., Parajka, J., Schijven, J., Sommer, R., Cervero-Arago, S., Lindner, G., Zoufal-Hruza, C.M., Linke, R., Savio, D., Ixenmaier, S.K., Kirschner, A.K.T., Kromp, H., Blaschke, A.P., Farnleitner, A.H., 2021. Modelling the interplay of future changes and wastewater management measures on the microbiological river water quality considering safe drinking water. Science of the Total Environment 768: 144278, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144278. *contributed equally
Derx, J., Demeter, K., Linke, R., Cervero-Aragó, S., Lindner, G., Stalder, G., Schijven, J., Sommer, R., Walochnik, J., Kirschner, A.K.T., Komma, J., Blaschke, A.P. & Farnleitner, A.H., 2021. Genetic Microbial Source Tracking Support QMRA Modeling for a Riverine Wetland Drinking Water Resource. Frontiers in Microbiology 12, 668778
Copyright
TU Wien, ICC Water & Health, Austria
National Institute for Public Health & the Environment (RIVM) / University of Utrecht,
The Netherlands
Supported by
Disclaimer
QMRAcatch has been developed with greatest care by RIVM and TUW. RIVM and TUW accept no claims for any direct or indirect damage, including financial loss, caused by any errors in the program or by misuse or misinterpretation of the program and the results produced by the program.


